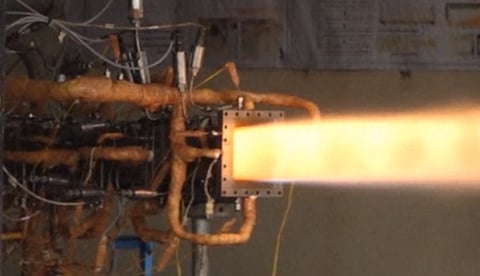

NEW DELHI: The DRDO has developed and successfully carried out the ground test of the long-duration Supersonic Combustion Ramjet, or Scramjet-powered hypersonic technology.
The Ministry of Defence, without giving the specific date of the test, said that "DRDL recently developed these technologies and demonstrated a cutting-edge Active Cooled Scramjet Combustor ground test for 120 seconds for the first time in India."
The successful ground test marks a crucial milestone in developing next-generation hypersonic missiles, it added.
The Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) is a Hyderabad-based laboratory of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
The key to hypersonic vehicles is Scramjets, which are air-breathing engines capable of sustaining combustion at supersonic speeds without using any moving parts.
Hypersonic missiles are a class of advanced weaponry that travel at speeds greater than Mach 5, i.e., five times the speed of sound or more than 5,400 km/hr.
"These advanced weapons have the potential to bypass existing Air Defence Systems and deliver rapid and high-impact strikes. Several nations, including the USA, Russia, India, and China, are actively pursuing Hypersonic technology," the MoD said.
The ground test of the scramjet combustor showcased several notable achievements, demonstrating its potential for operational use in hypersonic vehicles, like successful ignition and stable combustion.
"Ignition in a scramjet engine is like 'keeping a candle lit in a hurricane'. The scramjet combustor incorporates an innovative flame stabilisation technique that holds continuous flame inside the combustor with air speed in excess of 1.5 km/s."
For the successful development, the MoD said, "Many novel and promising ignition & flame-holding techniques were studied through many ground tests in arriving at the Scramjet Engine configuration. Advanced Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation tools were used for their evaluation & performance prediction.
The indigenous development of endothermic scramjet fuel, the first time in India, jointly by DRDL and industry, is central to this breakthrough. The fuel offers dual benefits of significant cooling improvement and ease of ignition," added the MoD. The team developed a special manufacturing process to achieve stringent fuel requirements of DRDL at an industrial scale.
Another key achievement is the development of a state-of-the-art Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) which is designed to withstand extreme temperatures encountered during hypersonic flight.
A new advanced ceramic TBC, having high thermal resistance & capable of operating beyond the melting point of steel, has been jointly developed by DRDL and the Department of Science & Technology (DST) Laboratory. The coating is applied inside the scramjet engine using special deposition methods that enhance their performance and longevity.
With demonstrated capabilities in stable combustion, enhanced performance, and advanced thermal management, this breakthrough sets the stage for next-generation hypersonic missiles.
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh has complimented DRDO and the industry for the successful Scramjet Engine Ground Test. "The achievement marks a crucial milestone in the development of next-generation hypersonic missiles," he said.
TNIE reported in 2022, quoting the Brahmos CEO, that India will have the first hypersonic missile in its arsenal in the next six years. At present, only a few countries, like the US, Russia, and China, have hypersonic missiles
Towards the process of attaining hypersonic speed, India had successfully tested the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV) by integrating scramjet engine technology.