
CHANDIGARH: Farmers in Punjab are not solely responsible for the region’s worsening air quality, as stubble-burning incidents are rising in both Indian and Pakistan's Punjab. Experts say Pakistan’s contribution to pollution is significant, with farm fires much higher there compared to India.
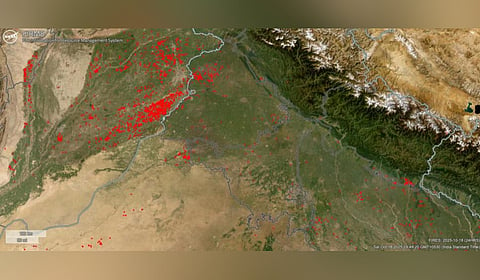
Dr Ravindra Khaiwal, Professor of Environmental Health at PGIMER Chandigarh and nodal officer for the Centre of Excellence on Climate Change and Air Pollution, said recent satellite analysis shows a 10-fold difference in stubble-burning hotspots: between October 9 and 18, Pakistans Punjab recorded 2,009 farm fires, while Indian Punjab had only 189.
The main hotspots in Pakistan's Punjab are Okara, Kasur, and Pakpattan, with Okara alone accounting for nearly 35% of all detected fires. Northwest-to-southeast wind patterns, combined with the flat terrain of the Punjab plains, allow smoke and fine particulate matter to travel freely into southeastern India, worsening air quality.
During the winter months, air pollution intensifies across the Indo-Gangetic plains due to the interplay of meteorological and human factors. The lack of rainfall, which normally helps clean the air, and soil resuspension from loosened agricultural land, adds to particulate loading in both urban and rural areas.
Dr Khaiwal emphasised that air pollution does not respect geopolitical boundaries and called for coordinated transboundary strategies. While Indian states like Punjab and Haryana have successfully controlled agricultural residue fires, similar measures are needed in Pakistan's Punjab.
Although stubble-burning incidents in Indian Punjab have declined, air quality levels have not improved correspondingly. Some fires may occur in conditions that evade satellite detection. Recent satellite images show thick smoke plumes drifting eastward, indicating a wider regional issue.
According to official records, 33 stubble-burning incidents were reported yesterday in the state, the highest this kharif season. A total of 241 farm fire incidents have been recorded so far, largely due to delayed paddy harvesting. Tarn Taran reported 23 new cases, while Amritsar recorded three, bringing the total incidents in Tarn Taran to 88 and in Amritsar to 80.
The worst air quality index (AQI) yesterday was in Mandi Gobindgarh (231), followed by Jalandhar (148), Ludhiana (116), and Patiala (101). There has been an 83% decrease in stubble-burning cases compared to the same period in previous years, when 1,348 and 1,407 incidents were reported from September 15 to October 18 in 2024 and 2023, respectively.
The Punjab government has decided to take stricter action against farmers who burn crop residue. District officials have been instructed to withdraw government scheme benefits from violators, including pensions and even arms licenses. Anganwadi workers are being deployed to spread awareness, and announcements are being made from religious places, mainly Gurdwaras. Students are also being sensitised to discourage parents from burning stubble.
Police have registered 119 FIRs under Section 223 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita for disobedience related to stubble burning. The Revenue Department has made 81 “red entries” in the land records of violators. The Punjab Pollution Control Board has imposed fines totalling Rs 5.15 lakh in 104 cases, of which Rs 3.65 lakh has been recovered.